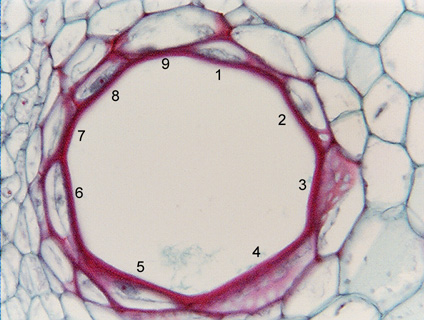
 Fig.
7.5-3. Transverse section of a vessel element in
muskmellon (Cucumis). This vessel element is so much larger than all
surrounding cells that it has 9 contact faces
in this section alone (the surrounding cells are probably shorter than the
vessel element, so if we could see the entire surface, there might be more than
20 contact faces). However, when this vessel element was first formed, is was
just a small parenchyma cell about the same size as surrounding cells and
probably with only about five or six contact faces (if all cells are about the
same size, a transverse section would show about six contact faces – like a
honeycomb). As it enlarged, it pushed the surrounding
cells apart and formed new contacts with cells that had originally not been next
to it. Despite the fact that these cell-cell contacts were made by
cells pushing up against each other (rather than being formed by a cell plate
during cell division), they still are able to form pit-pairs.
Fig.
7.5-3. Transverse section of a vessel element in
muskmellon (Cucumis). This vessel element is so much larger than all
surrounding cells that it has 9 contact faces
in this section alone (the surrounding cells are probably shorter than the
vessel element, so if we could see the entire surface, there might be more than
20 contact faces). However, when this vessel element was first formed, is was
just a small parenchyma cell about the same size as surrounding cells and
probably with only about five or six contact faces (if all cells are about the
same size, a transverse section would show about six contact faces – like a
honeycomb). As it enlarged, it pushed the surrounding
cells apart and formed new contacts with cells that had originally not been next
to it. Despite the fact that these cell-cell contacts were made by
cells pushing up against each other (rather than being formed by a cell plate
during cell division), they still are able to form pit-pairs.