Up
Primary xylem
Oak wood
Leaf vein
Vein ends
Bean seed
Pine tracheids, xs
Fern TE, xs
Fern, TE, mag
Annular walls
Annular, stretched
Annular, narrow
Scalariform walls
Scalar., narrow
CBP, pine
CBP, dicot
CBP, irregular
Contact faces
Pits, side view
CBP, pine, xs
CBP,angio, xs
CBP, fern, xs
Contact face, xs
Simple perf. plate 1
Simple perf. plate 2
Pitted perf. plate
Perf. plate & helix
Perf. plate, face
Perf. plate, mag
Perf. plate, section
Perf. plate rim
Perf. plate & wall
Scalariform Per plate
Primary xylem
Vessel sizes
Fern TE
Pine needle
VE precursor, ls
Protoxylem
9 Contact faces
VE precursor, xs
Precursor 2
Torn vessel
Torn vessel 2
| |
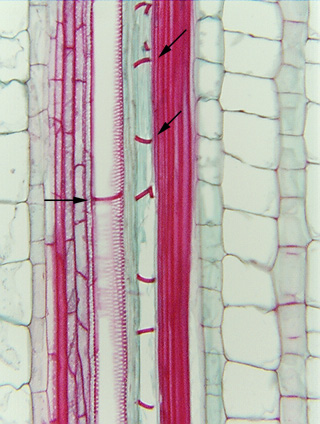 Fig.
7.2-2. Magnification of corn vessel element with annular
secondary walls. These secondary walls are very far apart because the
vessel element was stretched by the surrounding tissues after the element was
mature. It is difficult to tell if the primary wall of this vessel element is
still intact: if it were definitely functional, all the rings should be parallel
to each other, having the same tilt. In histological slides of mature stems,
vessel elements with annular secondary walls have often been torn apart by
internode expansion. Fig.
7.2-2. Magnification of corn vessel element with annular
secondary walls. These secondary walls are very far apart because the
vessel element was stretched by the surrounding tissues after the element was
mature. It is difficult to tell if the primary wall of this vessel element is
still intact: if it were definitely functional, all the rings should be parallel
to each other, having the same tilt. In histological slides of mature stems,
vessel elements with annular secondary walls have often been torn apart by
internode expansion.
Just
to the left is another vessel whose elements have pitted secondary walls (the
pits look like small white dots). It appears to have an annular ring also, but
that is the perforation plate between two vessel elements (more details on
perforation plates are given in later figures in this chapter).
|
 Fig.
7.2-2. Magnification of corn vessel element with annular
secondary walls. These secondary walls are very far apart because the
vessel element was stretched by the surrounding tissues after the element was
mature. It is difficult to tell if the primary wall of this vessel element is
still intact: if it were definitely functional, all the rings should be parallel
to each other, having the same tilt. In histological slides of mature stems,
vessel elements with annular secondary walls have often been torn apart by
internode expansion.
Fig.
7.2-2. Magnification of corn vessel element with annular
secondary walls. These secondary walls are very far apart because the
vessel element was stretched by the surrounding tissues after the element was
mature. It is difficult to tell if the primary wall of this vessel element is
still intact: if it were definitely functional, all the rings should be parallel
to each other, having the same tilt. In histological slides of mature stems,
vessel elements with annular secondary walls have often been torn apart by
internode expansion.