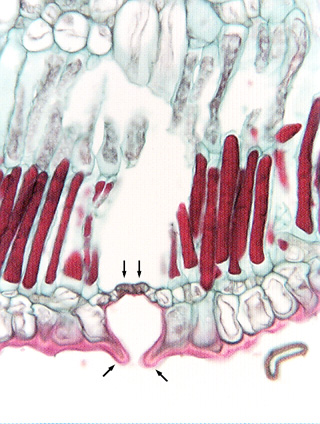
 Fig.
10.3-17. Transverse section of leaf of Hakea suaveolens
(Australian, in the Proteaceae; no common name). The stoma here (vertical arrows
indicate the two guard cells) is not as protected as those of the crypts of
oleander or the grooves of yucca, but they
are protected by subsidiary cells that have papillae that arch across the stoma,
creating a mini-depression. This will tend to retain escaped water, giving it
time to diffuse back into the stoma instead of being immediately blown away by a
breeze.
Fig.
10.3-17. Transverse section of leaf of Hakea suaveolens
(Australian, in the Proteaceae; no common name). The stoma here (vertical arrows
indicate the two guard cells) is not as protected as those of the crypts of
oleander or the grooves of yucca, but they
are protected by subsidiary cells that have papillae that arch across the stoma,
creating a mini-depression. This will tend to retain escaped water, giving it
time to diffuse back into the stoma instead of being immediately blown away by a
breeze.
The cuticle covers all exposed surfaces of the epidermis cells, even inside the depression formed by the subsidiary cells. The cuticle is quite thin on the guard cells themselves.